The U.S. State Department will work with the Department of Homeland Security to aggressively revoke visas for Chinese students
Chinese students studying in the United States are facing uncertainty regarding their futures following the announcement by U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio on Wednesday, which indicated that the visas of certain students would be revoked. The U.S. is poised to revoke visas for some Chinese students, particularly those engaged in “critical fields” and those with ties to the Chinese Communist Party, as outlined in the announcement.

China represents the second-largest group of origin for international students in the United States, following India. In the academic year 2023-2024, over 270,000 international students hailed from China, accounting for approximately a quarter of all foreign students in the U.S.
In the 2023-24 academic year, around 277,000 Chinese students were studying in the United States, making China the second-largest source country for international students behind India. While this number represents a significant portion of international students in the U.S., it’s also important to note that the number of Chinese students has declined from a peak of over 370,000 in 2019, partly due to rising geopolitical tensions and heightened U.S. government scrutiny.
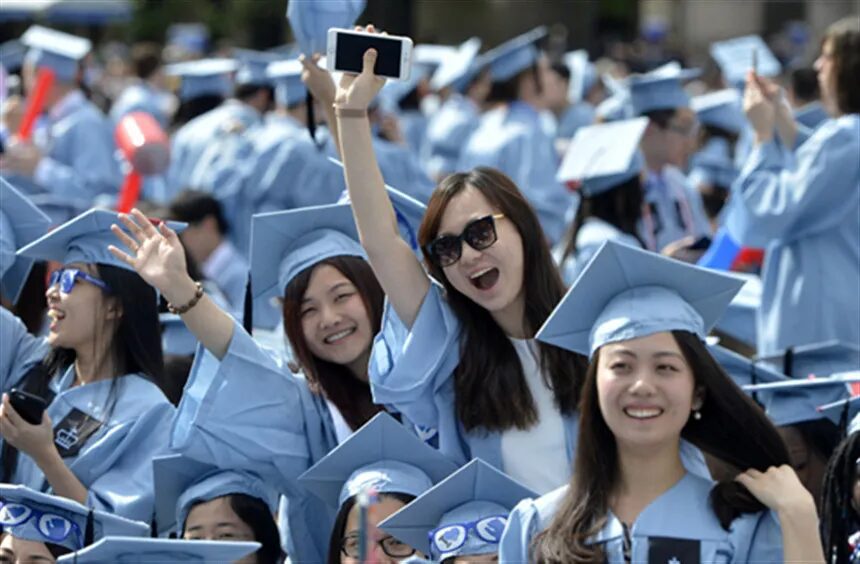

This is a “new version of Chinese Exclusion Act,” said Linqin, a Chinese student at Johns Hopkins University, who asked to be identified only by his first name out of fear of retaliation. He was referring to a 19th-century law that prohibited Chinese from immigrating to the U.S. and banned Chinese people already in the U.S. from getting citizenship. He said Wednesday was the first time he thought about leaving the U.S. after spending one third of his life here.
If implemented across a significant portion of the hundreds of thousands of Chinese university students in the United States, this action could significantly undermine a vital source of revenue for American educational institutions and critically impact the flow of talent to U.S. technology firms.
Key points about Chinese students in America:
- Significant Presence: Chinese students make up a substantial portion of the international student population in the U.S., often being the second-largest source country.
- Historical Decline: The number of Chinese students has been declining in recent years, though it remains a large number.
- Motivations: Many Chinese students choose to study in the U.S. seeking a high-quality education, a different cultural experience, and more freedom in their choice of study, according to a study by the China Data Lab.
- Government Scrutiny and Visa Issues:The U.S. government has been increasing its scrutiny of Chinese students and researchers, and some have had their visas revoked, particularly those studying in “critical fields” like STEM.
- Impact of COVID-19: The COVID-19 pandemic also had a significant impact on the number of international students, including Chinese students, entering the U.S.
- Growing Geopolitical Tensions: Rising geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and China have also contributed to the decline in the number of Chinese students, according to news reports.
- Continued Interest: Despite the challenges, many Chinese students still see the U.S. as a desirable destination for higher education, especially for STEM fields.
- Focus on STEM: Many Chinese students, particularly those interested in STEM fields, continue to see the U.S. as a leading location for these fields.
- Concerns about Discrimination: Some Chinese students have expressed concerns about discrimination and bias, particularly in light of the U.S. government’s increased scrutiny and visa revocations.
- Continued Support for American Institutions: Many Chinese alumni remain connected to their American institutions, contributing to alumni associations and financial donations, according to a study by US-China Education Trust.
